7.1 二叉树的广度优先搜索
二叉树的广度优先搜索是从上到下按层数遍历二叉树.
通常使用队列来实现二叉树的广度优先搜索:
- 将根节点放入队列
- 从队列中取出节点进行遍历
- 若节点存在子节点, 则将子节点放入队列中, 重复步骤 2)
由于先入先出的特性, 二叉树的节点按照从左至右的顺序进入队列, 因此可以很容易的直到每层的最左/右的节点, 或者每层的最值等.
如果涉及到二叉树的层相关的问题, 可以使用广度优先搜索来解决.
7.3.1 问题43: 在完全二叉树中添加节点
完全二叉树是每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大,第
n层有2^(n-1)个节点)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。设计一个用完全二叉树初始化的数据结构
CBTInserter,它支持以下几种操作:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)使用根节点为root的给定树初始化该数据结构;CBTInserter.insert(int v)向树中插入一个新节点,节点类型为TreeNode,值为v。使树保持完全二叉树的状态,并返回插入的新节点的父节点的值;CBTInserter.get_root()将返回树的根节点。示例 1:
输入:inputs = ["CBTInserter","insert","get_root"], inputs = [[[1]],[2],[]] 输出:[null,1,[1,2]]示例 2:
输入:inputs = ["CBTInserter","insert","insert","get_root"], inputs = [[[1,2,3,4,5,6]],[7],[8],[]] 输出:[null,3,4,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]]提示:
- 最初给定的树是完全二叉树,且包含
1到1000个节点。- 每个测试用例最多调用
CBTInserter.insert操作10000次。- 给定节点或插入节点的每个值都在
0到5000之间。
7.3.1.1 分析
概念
满二叉树
A full binary tree is a tree in which every node has either 0 or 2 children.
完全二叉树 (Complete Binary Tree, CBT)
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible.
分析
首先, 根据完全二叉树的定义:
- 除了最后一层外, 所有的层数节点都是满的(第n层有个节点)
- 最后一层的节点, 尽量向左靠拢
那么要插入一个节点, 在最后一层从左到右找到空缺的为止插入即可.
可以看出, 在完全二叉树中添加节点的顺序是按照广度优先搜索的顺序来的.
那么, 问题就转换成了: 使用广度优先搜索, 找出第一个没有左/右子节点的节点, 将新节点插入.
流程
- 构建Inserter: 广度优先搜索, 寻找没有左/右子节点的节点, 加入队列
- 插入节点:
- 若插入位置为左节点, 返回父节点
- 若插入位置为右节点:
- 将父节点从队列中删除(不满足入队条件)
- 左右子节点入队
7.3.1.2 题解
TC: O(n), 广度优先搜索遍历一遍二叉树
SC: O(n), 需要队列存储节点
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
type CBTInserter struct {
queue []*TreeNode
root *TreeNode
}
func Constructor43(root *TreeNode) CBTInserter {
// 使用广度优先搜索, 查找不含左/右子节点的节点
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root)
// 广度优先搜索
for len(queue) > 0 && queue[0].Left != nil && queue[0].Right != nil {
// 出列
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// 添加左右节点
queue = append(queue, node.Left, node.Right)
}
return CBTInserter{
queue: queue,
root: root,
}
}
func (ci *CBTInserter) Insert(v int) int {
node := &TreeNode{Val: v}
// 获取最左边的有空缺的节点
parent := ci.queue[0]
if parent.Left == nil { // 插入左边
parent.Left = node
} else { // 插入右边
parent.Right = node
// 此时左右节点都存在, 出队
ci.queue = ci.queue[1:]
// 子节点入队
ci.queue = append(ci.queue, parent.Left, parent.Right)
}
return parent.Val
}
func (ci *CBTInserter) GetRoot() *TreeNode {
return ci.root
}
7.3.2 问题44: 二叉树每层的最大值
给定一棵二叉树的根节点
root,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。示例1:
输入: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] 输出: [1,3,9] 解释: 1 / \ 3 2 / \ \ 5 3 9示例2:
输入: root = [1,2,3] 输出: [1,3] 解释: 1 / \ 2 3示例3:
输入: root = [1] 输出: [1]示例4:
输入: root = [1,null,2] 输出: [1,2] 解释: 1 \ 2示例5:
输入: root = [] 输出: []提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,10^4]-2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
7.3.2.1 分析&题解
涉及到二叉树的层, 可以使用队列进行广度优先搜索.
一个队列
使用一个队列, 需要引入两个变量cur, next, 分别对当前层和下一层节点进行计数:
- 根节点入队, cur++; 根节点出队, cur--
- 子节点入队, next++
- 当cur为0, 表示当前层已经遍历完毕; 可找出当前层的最大值; 将next赋值给cur, 重新开始下一层.
func largestValuesWithSingleQ(root *TreeNode) []int {
result := make([]int, 0)
// 边界条件
if root == nil {
return result
}
// 当前和下一层的节点数
cur, next := 0, 0
// 每层最大节点
maxVal := math.MinInt
// 广度优先搜索
q := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
q = append(q, root)
cur++
for len(q) > 0 {
// 当前层节点出队
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
maxVal = max(maxVal, node.Val)
cur--
// 添加下一层
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
next++
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
next++
}
// 当前层结束
if cur == 0 {
result = append(result, maxVal)
maxVal = math.MinInt
cur = next
next = 0
}
}
return result
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
两个队列
将不同层的节点放入两个队列中.
- 将当前层节点放入q1
- 下一层节点放入q2
- 当q1为空时, 当前层已经遍历完毕; q2赋值给q1, 重置q2, 开始新的一层
func largestValuesWithDoubleQ(root *TreeNode) []int {
result := make([]int, 0)
// 边界
if root == nil {
return result
}
// 双队列
q1 := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
q2 := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
// 最大值
maxVal := math.MinInt
// 广度优先遍历
q1 = append(q1, root)
for len(q1) > 0 {
// 出队
node := q1[0]
q1 = q1[1:]
maxVal = max(maxVal, node.Val)
// 下一层入队
if node.Left != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Right)
}
// 当前层结束
if len(q1) == 0 {
result = append(result, maxVal)
maxVal = math.MinInt
// 开始下一层
q1, q2 = q2, q1
}
}
return result
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
7.3.3 问题45: 二叉树最底层左边的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
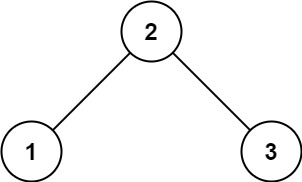
img 输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 1示例 2:
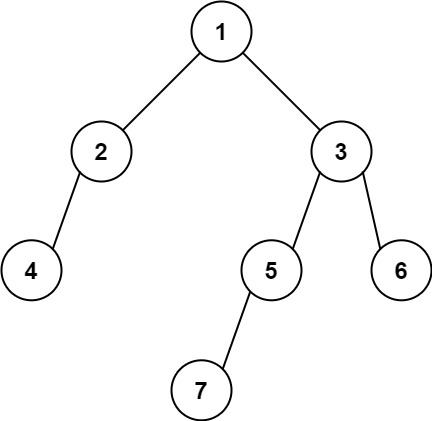
img 输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] 输出: 7提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,10^4]-2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
7.3.3.1 分析&题解
和寻找每层最大值类似, 涉及到层需要使用广度优先遍历, 又因为需要统计每层那么可以使用双队列来解决.
func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int {
bottomVal := root.Val
// 广度优先
q1 := make([]*TreeNode, 0) // 当前层
q2 := make([]*TreeNode, 0) // 下一层
q1 = append(q1, root)
for len(q1) > 0 {
// 出队
node := q1[0]
q1 = q1[1:]
// 下一层入队
if node.Left != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Right)
}
// 当前层结束
if len(q1) == 0 {
// 下一层
q1, q2 = q2, q1
if len(q1) > 0 {
// 下一层最左
bottomVal = q1[0].Val
}
}
}
return bottomVal
}
7.3.4 问题46: 二叉树的右侧视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。示例 1:
img 输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4] 输出: [1,3,4]示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3] 输出: [1,3]示例 3:
输入: [] 输出: []提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,100]-100 <= Node.val <= 100
7.3.4.1 分析&题解
右侧视图实际上是寻找每层最右侧的节点, 那么使用双队列+广度优先搜索即可解决.
func rightSideView(root *TreeNode) []int {
result := make([]int, 0)
// 边界
if root == nil {
return result
}
// 广度优先
q1 := make([]*TreeNode, 0) // 当前层
q2 := make([]*TreeNode, 0) // 下一层
q1 = append(q1, root)
for len(q1) > 0 {
// 出队
node := q1[0]
q1 = q1[1:]
// 下层入队
if node.Left != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q2 = append(q2, node.Right)
}
// 当前层结束
if len(q1) == 0 {
// 最右侧节点
result = append(result, node.Val)
// 开始下一层
q1, q2 = q2, q1
}
}
return result
}