同步原语与锁
...大约 7 分钟
1. Mutex
数据结构
type Mutex struct {
state int32
sema uint32
}
state:互斥锁状态sema:信号量
状态
互斥锁的状态通过state的二进制位表示,默认状态所有位为0:

mutexLocked:锁定状态mutexWoken:从正常模式被唤醒mutexStarving:饥饿状态waitersCount:当前锁上等待的 goroutine 的个数
模式
- 正常模式:goroutine 按照 FIFO 顺序获取锁 刚被唤起的 Goroutine 与新创建的 Goroutine 竞争时,大概率会获取不到锁;一旦 Goroutine 超过 1ms 没有获取到锁,它就会将当前互斥锁切换饥饿模式,以保证互斥锁的公平性
- 饥饿模式: 互斥锁会直接交给等待队列最前面的 Goroutine
- 新的 Goroutine 在该状态下不能获取锁、也不会进入自旋状态,只会在队列的末尾等待。若一个 Goroutine 获得了互斥锁并且它在队列的末尾或者它等待的时间少于 1ms,那么当前的互斥锁就会切换回正常模式。
加锁
func (m *Mutex) Lock() {
if atomic.CompareAndSwapInt32(&m.state, 0, mutexLocked) {
return
}
m.lockSlow()
}
- 当锁的状态是 0 时,将
mutexLocked位置成 1 - 状态不是 0 时,
sync.Mutex.lockSlow通过自旋(Spinnig)等方式等待锁的释放
sync.Mutex.lockSlow流程如下:
- 判断当前 Goroutine 能否进入自旋
- 通过自旋等待互斥锁的释放
- 计算互斥锁的最新状态
- 更新互斥锁的状态并获取锁
解锁
func (m *Mutex) Unlock() {
new := atomic.AddInt32(&m.state, -mutexLocked)
if new != 0 {
m.unlockSlow(new)
}
}
- 若该
sync/atomic.AddInt32返回的新状态等于 0,当前 Goroutine 就成功解锁 - 若该函数返回的新状态不等于 0,则调用
sync.Mutex.unlockSlow开始慢解锁
慢解锁流程:
- 正常模式下:
- 若互斥锁不存在等待者或者互斥锁的
mutexLocked、mutexStarving、mutexWoken状态不都为 0,那么当前方法可以直接返回,不需要唤醒其他等待者 - 若互斥锁存在等待者,会通过
sync.runtime_Semrelease唤醒等待者并移交锁的所有权
- 若互斥锁不存在等待者或者互斥锁的
- 饥饿模式下: 直接调用
sync.runtime_Semrelease将当前锁交给下一个正在尝试获取锁的等待者,等待者被唤醒后会得到锁,在这时互斥锁还不会退出饥饿状态
小结
加锁过程:
- 若互斥锁处于初始化状态,会通过置位
mutexLocked加锁 - 若互斥锁处于
mutexLocked状态并且在普通模式下工作,会进入自旋,执行 30 次PAUSE指令消耗 CPU 时间等待锁的释放 - 若当前 Goroutine 等待锁的时间超过了 1ms,互斥锁就会切换到饥饿模式
- 互斥锁在正常情况下会通过
runtime.sync_runtime_SemacquireMutex将尝试获取锁的 Goroutine 切换至休眠状态,等待锁的持有者唤醒 - 若当前 Goroutine 是互斥锁上的最后一个等待的协程或者等待的时间小于 1ms,那么它会将互斥锁切换回正常模式
解锁过程:
- 当互斥锁已经被解锁时,调用
sync.Mutex.Unlock会直接抛出异常 - 当互斥锁处于饥饿模式时,将锁的所有权交给队列中的下一个等待者,等待者会负责设置
mutexLocked标志位 - 当互斥锁处于普通模式时:
- 若没有 Goroutine 等待锁的释放或者已经有被唤醒的 Goroutine 获得了锁,会直接返回
- 其他情况下会通过
sync.runtime_Semrelease唤醒对应的 Goroutine
2. RWMutex
数据结构
type RWMutex struct {
w Mutex
writerSem uint32
readerSem uint32
readerCount int32
readerWait int32
}
w:复用互斥锁writerSem:写等待读信号readerSem:读等待写信号readerWait:当前操作被阻塞时,等待的读操作的个数readerCount存储了当前正在执行的读操作数量
写锁
获取
func (rw *RWMutex) Lock() {
rw.w.Lock()
r := atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerCount, -rwmutexMaxReaders) + rwmutexMaxReaders
if r != 0 && atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerWait, r) != 0 {
runtime_SemacquireMutex(&rw.writerSem, false, 0)
}
}
- 获取写锁,若已被获取则等待
- 阻塞后续读操作
- 等待所有的读操作结束后,唤醒当前 goroutine
获取写锁时会先阻塞写锁的获取,后阻塞读锁的获取,这种策略能够保证读操作不会被连续的写操作『饿死』。
释放
func (rw *RWMutex) Unlock() {
r := atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerCount, rwmutexMaxReaders)
if r >= rwmutexMaxReaders {
throw("sync: Unlock of unlocked RWMutex")
}
for i := 0; i < int(r); i++ {
runtime_Semrelease(&rw.readerSem, false, 0)
}
rw.w.Unlock()
}
- 将
reaerCount变为正数释放读锁 - 释放陷入因读锁陷入等待的 Gorotuine
- 释放写锁
读锁
获取
func (rw *RWMutex) RLock() {
if atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerCount, 1) < 0 {
runtime_SemacquireMutex(&rw.readerSem, false, 0)
}
}
readerCount若为负数,表示存在写锁,等待写锁释放
释放
func (rw *RWMutex) RUnlock() {
if r := atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerCount, -1); r < 0 {
rw.rUnlockSlow(r)
}
}
readerCount减一- 获取
readCount结果- 小于零,存在写锁,进入慢解锁
- 大于等于零,直接解锁
慢解锁:
func (rw *RWMutex) rUnlockSlow(r int32) {
if r+1 == 0 || r+1 == -rwmutexMaxReaders {
throw("sync: RUnlock of unlocked RWMutex")
}
if atomic.AddInt32(&rw.readerWait, -1) == 0 {
runtime_Semrelease(&rw.writerSem, false, 1)
}
}
- 减少获取锁的写操作等待的读操作数
readerWait - 在所有读操作都被释放之后触发写操作的信号量
writerSem,唤醒尝试获取写锁的 Goroutine
3. WaitGroup
数据结构
type WaitGroup struct {
noCopy noCopy
state1 [3]uint32
}
noCopy:保证变量不会被拷贝state1:存储状态和信号量
防止拷贝
sync.noCopy 是一个特殊的私有结构体,tools/go/analysis/passes/copylock 包中的分析器会在编译期间检查被拷贝的变量中是否包含 sync.noCopy 或者实现了 Lock 和 Unlock 方法,若包含该结构体或者实现了对应的方法就会报出以下错误:
func main() {
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
yawg := wg
fmt.Println(wg, yawg)
}
$ go vet proc.go
./prog.go:10:10: assignment copies lock value to yawg: sync.WaitGroup
./prog.go:11:14: call of fmt.Println copies lock value: sync.WaitGroup
./prog.go:11:18: call of fmt.Println copies lock value: sync.WaitGroup
状态
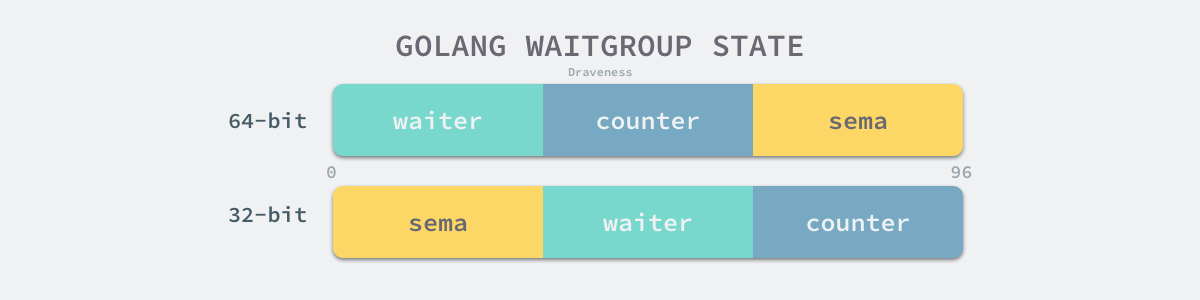
state1是总共占用 12 字节的数组,存储当前结构体的状态,在64位和32位机上表现不同:
Add
func (wg *WaitGroup) Add(delta int) {
statep, semap := wg.state()
state := atomic.AddUint64(statep, uint64(delta)<<32)
v := int32(state >> 32)
w := uint32(state)
if v < 0 {
panic("sync: negative WaitGroup counter")
}
if v > 0 || w == 0 {
return
}
*statep = 0
for ; w != 0; w-- {
runtime_Semrelease(semap, false, 0)
}
}
- 计数器只能为非负数
- 负数会引起 panic
- 计数器归零,唤醒等待中的 Goroutine
Done
实际复用Add(-1)
Wait
func (wg *WaitGroup) Wait() {
statep, semap := wg.state()
for {
state := atomic.LoadUint64(statep)
v := int32(state >> 32)
if v == 0 {
return
}
if atomic.CompareAndSwapUint64(statep, state, state+1) {
runtime_Semacquire(semap)
if +statep != 0 {
panic("sync: WaitGroup is reused before previous Wait has returned")
}
return
}
}
}
- 计数器大于 0 ,则进入阻塞
- 计数器归零,则被唤醒
4. Once
数据结构
type Once struct {
done uint32
m Mutex
}
done:表示代码是否被执行过m:互斥锁
Do
func (o *Once) Do(f func()) {
if atomic.LoadUint32(&o.done) == 0 {
o.doSlow(f)
}
}
func (o *Once) doSlow(f func()) {
o.m.Lock()
defer o.m.Unlock()
if o.done == 0 {
defer atomic.StoreUint32(&o.done, 1)
f()
}
}
- 若已经执行过则直接返回
- 获取互斥锁
- 执行函数
done加一,表示已执行
5. Cond
数据结构
type Cond struct {
noCopy noCopy
L Locker
notify notifyList
checker copyChecker
}
noCopy:保证编译期不会被拷贝copyChecker:禁止运行时拷贝L:保护后续字段notify: Goroutine 链表
type notifyList struct {
wait uint32
notify uint32
lock mutex
head *sudog
tail *sudog
}
wait:当前等待的 goroutine 索引notify:已经通知到的 goroutine 索引
Wait
func (c *Cond) Wait() {
c.checker.check()
t := runtime_notifyListAdd(&c.notify) // runtime.notifyListAdd 的链接名
c.L.Unlock()
runtime_notifyListWait(&c.notify, t) // runtime.notifyListWait 的链接名
c.L.Lock()
}
func notifyListAdd(l *notifyList) uint32 {
return atomic.Xadd(&l.wait, 1) - 1
}
使当前 goroutine 陷入休眠:
- 等待计数器加一
- 解锁
- 等待唤醒
- 加锁
runtime_notifyListWait
func notifyListWait(l *notifyList, t uint32) {
s := acquireSudog()
s.g = getg()
s.ticket = t
if l.tail == nil {
l.head = s
} else {
l.tail.next = s
}
l.tail = s
goparkunlock(&l.lock, waitReasonSyncCondWait, traceEvGoBlockCond, 3)
releaseSudog(s)
}
获取当前 goroutine 并将其追加至通知链表的尾部
Singal
唤醒等待队列的最前面的 goroutine
func (c *Cond) Signal() {
c.checker.check()
runtime_notifyListNotifyOne(&c.notify)
}
Broadcase
唤醒队列中全部的 goroutine
func (c *Cond) Broadcast() {
c.checker.check()
runtime_notifyListNotifyAll(&c.notify)
}
小结
Wait:调用前需要加锁,否则会触发 panicSignal:唤醒等待队列最前面的(链表首部)的goroutineBroadcase:唤醒全部的 goroutine
Reference
Powered by Waline v2.15.2
